What are Tonsils?
The tonsils are two structures at the back of the throat, one on each side. They are lumps of tissue that are oval in shape and resemble some glands. The exterior of the tonsils is made up of pink mucous membranes, similar to those in the mouth. Inside the tonsil tissue, there are cells that protect against infection called lymphocytes, making part of the lymphatic system.
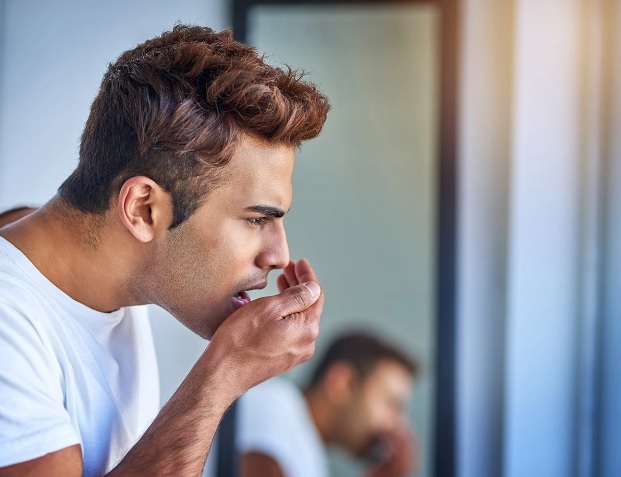

Because everyone is unique in the way their body fights, tonsils can be problematic for some people. Many medical professionals believe that the tonsils act as a barrier that prevents the spread of bacteria or viruses through the throat, trapping them in the body. However, for some people, the tonsils don’t work as smoothly as they should, causing more trouble than they should.
In the past, a common surgery for people with tonsil problems was a tonsillectomy, which is an operation to remove the tonsils. Doctors recommend this as soon as a patient shows any type of signs of tonsil dysfunction. At present, however, this procedure is uncommon, and studies have shown that removing tonsils does not necessarily make patients less susceptible to infection. Today, this procedure is recommended for those who suffer from recurrent tonsil infections or who suffer from discomfort due to oversized tonsils.
Medical Conditions of the Tonsils
The most common diseases associated with the tonsils are acute tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess, strep throat, enlarged tonsils, and tonsil stones.
1. Acute and Chronic Tonsillitis
As the name suggests, tonsillitis is a bacterial or viral infection of the tonsils that makes them swell and inflame. Some of the most common symptoms are sore throat, fever, headache, reddened tonsils, difficulty swallowing, voice changes, ear pain, throat blisters, and yellow abscesses in the tonsils . Depending on how long these symptoms last, tonsillitis may be acute, with symptoms lasting 3-4 days to 2 weeks, recurring if the patient has had multiple infections within a year, or if symptomsIf symptoms last for a long time, it is chronic.
2. Peritonsillar Abscess
An infection of the tonsils causes a pustule to form around the tonsils, pushing the tonsils toward the middle of the neck, where the uvula is (the dangling tissue visible at the back of the neck). This makes the whole area very painful and it is sometimes difficult to open the mouth. In the case of a peritonsillar abscess, it is advisable to drain it as soon as possible because if left untreated, the infection can spread the infection deeper into the neck, leading to some life-threatening complications (one of which is airway obstruction).
3. Strep Throat
Strep throat is an infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes or Group A Streptococcus. Usually more common in children, it affects the tonsils, making them red, swollen, painful, and in some cases, it can cause white or yellow pus to form on or around the tonsils. This is a serious condition that requires proper diagnosis and treatment because if left untreated it can lead to rheumatic fever, which affects the heart valves, joints and nervous system, or glomerulonephritis, which affects the kidneys. This usually happens later in life and most people are unaware at a young age that these can be serious complications from a poorly treated “just a simple cold”.
4. Enlarged Tonsils
Hypertrophic tonsils are enlarged tonsils that cause breathing disturbances, primarily affecting a person’s sleep patterns. This condition can lead to snoring or, in more severe cases, sleep apnea. Other symptoms can be agitated sleep, frequent awakenings, excessive sleepiness, or heart problems. Chronically enlarged tonsils can also lead to sinusitis , nasal congestion, or ear infections ( affecting the Eustachian tubes that connect the throat to the inner ear ). In some cases, this medical condition is also thought to be the cause of malocclusion, a gap between the upper and lower teeth dislocation.
5. Tonsil Stones
Tonsils are pieces of bacteria or debris that harden into small structures called tonsil stones. We will continue to delve deeper into the topic of tonsil stones.
Are These Diseases Contagious?
Much depends on what is causing the tonsil – related medical condition . For example, viral cases of tonsillitis, such as those caused by mononucleosis, are contagious. The same goes for bacterial strep throat. However, tonsillitis is less likely to be contagious if it is caused by a chronic condition (eg, sinusitis, chronic rhinitis).
Are Tonsil Stones Contagious?
Tonsil stones themselves are not contagious. However, they often co-occur with tonsillitis, which, as mentioned earlier, can be contagious depending on what is causing it.
Tonsil Stone Definition
Tonsil stones ( medically known as Tonsilloliths) are painful, hard structures located on or within the tonsils. They can be yellow or white and are usually part of the remains of bacteria or other types that have stuck to the tonsils.
Tonsil stones are calcified accumulations of cellular debris and bacteria found in the crypts of the tonsils. Tonsil stones are more adolescentscommon. Tonsils range in size from barely visible the size of a pea.
It is very rare for people to have large tonsil stones. Typically, people have one or several tonsil stones, but most of the time, people have only small structures in their tonsils that cause no symptoms.
Tonsil stones are calcifications that form in the recesses of the tonsils in the palate. Calcium salts alone or with other mineral salts make up these stones.
Tonsils can induce bad breath in the mouth. During bacterial metabolism, unpleasant – smelling chemicals such as volatile sulfur compounds and sulfur-derived gases are produced. When the amount of gas produced reaches a certain level, a characteristic sulfurous smell is produced.
Epidemiology
Tonsil stones, also known as tonsil concretions, affect up to 10% of the population and are usually caused by flare-ups of tonsillitis. Small stones in the tonsils are common, but true stones are not. They are more common in young adults and less common in children.
Tonsil stones can form at any age, however, they are more common in adults than in children. Some people form only one, but others may form multiple at the same time. Even if some people remove one, another will form elsewhere.
Causes of Tonsil Stones
In addition to having lymphocytes that fight bacteria and viruses, tonsils also have structures made up of hollows and nooks called crypts. These are where any type of debris such as bacteria, dead cells, saliva, food residue, and mucus get stuck and start to build up. Now, you may be asking yourself “how do tonsil stones form “. Well, over time, this buildup can harden or calcify the tonsils into tonsil stones. However, in this process is more common in patients with recurrent tonsillitis (usually chronic) or in patients whose tonsils have been inflamed for a long time.
Tonsil Stone Symptoms
Tonsil stones are sometimes difficult to see with the naked eye, even if they are quite large . However, these stones can cause a lot of trouble for people, some of the symptoms include:
Bad breath
Bad breath is one of the main signs of tonsil stones; tonsil stone bad breath is caused by bacteria and fungi that feed on debris buildup, causing a distinctive smell (tonsil stones odor); this particular odor is determined by high levels of volatile sulfur compounds in the breath that have been found in most patients with some type of tonsillitis.
Tonsil stone infection
Given that an infection of the tonsils can lead to the formation of tonsil stones; this makes it difficult to assess which of the two conditions is causing the sore throat; however, tonsil stones can cause a lot of discomfort and pain (tonsil stone pain), especially if the stones are large.
Coughing
Depending on size and location, tonsil stones can irritate the throat, causing patients to cough repeatedly.
White flakes
A physical symptom of tonsil stones is that they can be seen as white lumps on examination of the back of the throat (of course , keep in mind that some tonsil stones are so small that they can only be seen on an x-ray or found on a CT scan).
Dysphagia
Depending on the size and location of the tonsil stone it can cause difficulty swallowing, making eating or drinking painful.
Otalgia
This may be the result of a separate tonsil stone or a combination of tonsil stone and; if the patient has a tonsil stone, depending on the location of the tonsil, it can trigger some of the neural pathways commonly associated with the ear; therefore, the pain may also radiate into the ear, which is more of a sensation, a “false” pain, given the cause is located in the throat; however, if tonsil stones occur at the same time as tonsillitis, the ear Duo pain may also be caused by the latter, and tonsil infection may also spread to the ears.
Swollen tonsils
Tonsil stones can cause the tonsils to become inflamed, but they can also become infected, causing the tonsils to swell.
Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
Diagnosing tonsil stones depends the size and location of this calcified buildup. Usually, the diagnosis of tonsillitis is based on a physical examination. Your doctor will look at the back of your neck to assess the status of your tonsils (if they are red, inflamed, or have pus on or around them), take your temperature, and examine your nose and are there signs of an infection in the ear.
Make sure to differentiate tonsil stones from the white pus spots that are common. However, if stones are not visible and doctors suspect they may perform scans to confirm the diagnosis or to better assess the number, location, and size of stones.
In addition to a physical examination, your doctor may wish to perform some tests to determine the cause of the infection. The two most common tests are a throat swab to check for group A strep infection and a blood test, which is often used to diagnose mononucleosis.
Tonsil Stones vs. Tonsillitis
Don’t confuse the two! As we have seen before, tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils caused by bacteria or viruses, while tonsil stones can be the result of repeated tonsil infections.
Tonsil Stone Treatment
If tonsil stones are not bothersome, no treatment required. There is no specific treatment for tonsil stones, but you can treat symptoms before they cause you discomfort. In case of pain and swelling, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended.
However, if the tonsil stones are the result of tonsillitis, remember that the treatment options for the infection depend on its type: if it is bacterial , antibiotics are mandatory, if it is viral, it is not prescribed. Prescription pain relievers and good hydration are the preferred strategies for treatment.
Still, your doctor is able to assess your condition and combine your symptoms to better understand its cause, so don’t wait too long before consulting with a health care provider who can help you find the best way to relieve your symptoms.
Removal of Tonsil Stones
Cleared manually
It is not recommended to do it at home as it can lead to serious complications such as bleeding or infection from tonsil stones. If the stones grow large and cause severe discomfort, it is best to seek medical help, as there are minor surgeries aimed at removing tonsil stones.
Tonsil stone removal tool
A manual pressurized tonsil stone remover is also available. The water pressure of the manual tonsil stone remover can be adjusted according to the number of pumps, thus effectively removing tonsil stones.
Laser tonsil ablation and cryoablation for thawing
These procedures are used to remove and scar the tonsil crypts where the tonsil stones are located. While laser tonsil ablation uses a laser to achieve this result, cryoablation does not use any type of heat, achieving the same results but without the burning. These procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia with minimal discomfort and a very short recovery time.
Curettage
Larger tonsil stones may require curettage (scooping) or other methods of removal smaller pieces may still require extensive irrigation to completely flush away. Larger lesions may require local excision, however, these treatments may not be sufficient to reduce the foul-smelling breath commonly associated with this disease.
Tonsillectomy
Tonsil stones Tonsillectomy is a surgery aimed at the complete removal of the tonsils. In general, there are two main reasons for wanting to have your tonsils removed: the first reason is if your tonsils are dysfunctional making it difficult, especially during sleep; the second reason is if your throat is multiple infections over the course of a year, resulting in infection of the tonsils as well (tonsillitis). This is the most common procedure performed on children, but there have been cases of tonsil removal in adults.
Patients may experience sore throat and ear pain for several days after surgery, making recovery difficult. Another option is partial tonsillectomy using a laser, a procedure called tonsil crypt fusion, which closes the gaps in the tonsils where particles can collect and prevents tonsil stones from forming.
While in the past, tonsillectomy was recommended and performed almost immediately if someone showed any signs of a throat infection, the procedure is not as common now as it used to be. Healthcare professionals recommend tonsillectomy for patients with recurrent tonsil infections (chronic tonsillitis) that cause a lot of discomfort and disrupt activities of daily living.
Tonsil Stone Home Remedies
While there is no definitive treatment for tonsil stones, there are remedies and medical procedures that can help remove tonsil stones. Although tonsil stones do not cause much trouble most of the time, patients still want to have them removed, especially because they cause a bad tonsil stone smell. Another reason to remove tonsil stones is that they may become infected.
We list a list of treatments and procedures that can help treat tonsil stones at home.
1. Gargle
Gargling vigorously with warm, salty water is a good remedy for tonsil stones and can help relieve discomfort and pain, as well as the unpleasant smell the stones cause. What’s more, rinsing your mouth can also be useful in the event of a stuck tonsil stone, helping to loosen.
Mouthwash can be used instead of salt water when gargling . Make sure the mouthwash is alcohol-free, as alcohol can dry out the mucous membranes of the mouth, increase cell shedding and aggravate the development of tonsil stones. If available, use an oxygenating mouthwash, which helps prevent the growth of anaerobic bacteria that can cause tonsil stones and foul odor.
Gargling with warm salt water can also help relieve the pain of tonsillitis, which is often accompanied by tonsil stones. Rinsing vigorously every morning will keep the tonsil crypts open for all but the most stubborn tonsil stones.
2. Cough
Some people discover they have tonsil stones when they cough into a tissue. A persistent cough can also help loosen tonsil stones lodged in the throat.
3. Antibiotic
In general, antibiotics are not recommended for tonsil stones because they do not treat the cause. However, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to prevent bacterial infection of your tonsil stones. But keep in mind the side effects of antibiotics, and you should never take them without consulting a medical professional.
4. Hydrate
To avoid tonsil stones, stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Water can also help change the chemicals in your mouth by increasing natural saliva production.
5. Quit Smoking
Eliminate smoking and other tobacco products from your diet, as they may cause the bacteria in your throat to develop tonsil stones.
How to Prevent Tonsil Stones
The best thing you can do to prevent a viral or bacterial infection of your tonsils is to practice good hygiene. This means washing your hands frequently and avoiding sharing items (e.g. utensils, food, bottles, toothbrushes) that have come into contact with saliva or liquid with others. Also, if you feel unwell, avoid contact with others, always sneeze or cough into a tissue, wash or sanitize your hands, and consult your doctor about your symptoms.
To prevent tonsil stones from forming, you can take steps such as maintaining good and healthy oral hygiene (regular brushing and flossing ), not smoking or quitting, gargling with warm salt water after eating and staying hydrated. All of these bacteria and prevent tonsil buildup.
When to Worry About Tonsil Stones
Sure, they’re inconvenient and unpleasant, but how do you know if tonsil stones be treated by a doctor? It all comes down to the size and location of the stone, and your level of discomfort.
If you’re not sure, see your dentist and ask if you should consider having your tonsils removed. If you have persistent tonsil infections or tonsil stones, tonsillectomy may be the answer to treating recurring symptoms.
Conclusion
Tonsil stones are more common than we think, especially because sometimes they cause no symptoms. Good oral hygiene can prevent tonsil stones from developing, and if they still occur and cause discomfort, there are several ways that a doctor can remove them. Pay close attention to treatment recommendations as there is no specific treatment for tonsil stones (other than removing them) and don’t get caught up in the (over) use of antibiotics.
Patients with tonsillitis have increased halitosis and foreign body sensation. A tonsil stone is a stone that is also a living biofilm. Tonsil stone formation is caused by bacteria forming a three-dimensional structure with dormant bacteria in the middle acting as a continuous biofilm core.
The exact etiology and pathophysiology is not fully understood. Therefore, the current status of tonsil stones was studied and the detection of tonsil stones was performed using physical, chemical, and microbiological methods.